Water tanks are essential for storing and supplying clean water to households and businesses. However, these tanks can become contaminated with various harmful substances, leading to serious health risks. Common water tank contaminants include bacteria, viruses, and chemicals like lead and arsenic. These contaminants can enter the water supply through various means, such as rainwater runoff, organic matter, and improper tank maintenance. It is crucial to identify and eliminate these contaminants to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals who rely on the water stored in these tanks.
In addition to potentially harmful microorganisms and chemicals, another concern with water tank contaminants is the development of biofilms. These slimy layers of bacteria, algae, and other microorganisms can form on the walls of the tank and contaminate the water. Biofilms not only affect the quality of the water but also make it more difficult to clean and sanitize the tank effectively. In the upcoming sections of this article, we will discuss key strategies for identifying and eliminating common water tank contaminants, as well as preventive measures to maintain a clean and safe water supply. Stay tuned to learn how to protect yourself and your loved ones from the health risks associated with contaminated water tanks.
What you should know
1. Understand the common contaminants found in water tanks, including bacteria, algae, sediment, and chemical pollutants, which can pose health risks if not properly managed.
2. Regular maintenance and cleaning of water tanks are crucial for preventing the build-up of harmful contaminants and ensuring the quality of water for consumption.
3. Implementing a comprehensive water treatment system can help eliminate contaminants and improve the overall water quality in tanks, reducing the risk of health issues.
4. Monitoring water tank levels and conditions regularly can help detect any potential issues early on and address them promptly to prevent contamination and safeguard public health.
5. Educating individuals on the importance of water tank maintenance and addressing contamination risks is essential for promoting safe drinking water practices and protecting community well-being.
What are the common water tank contaminants and how can they be identified and eliminated to reduce health risks?
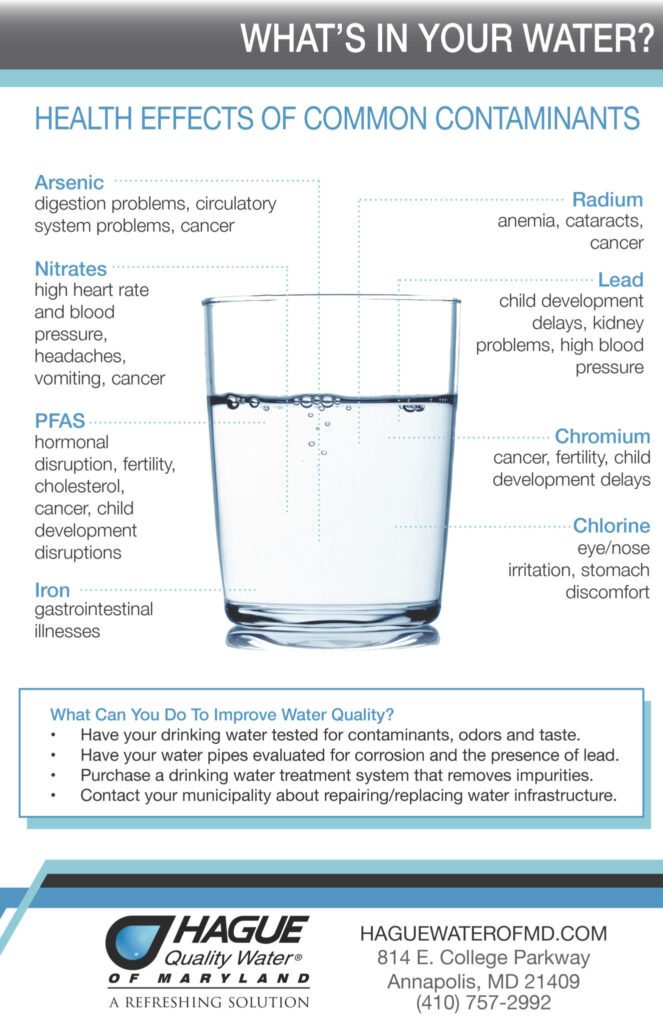
Water tank contaminants can include bacteria, viruses, parasites, heavy metals, and chemicals that can pose serious health risks if consumed. These contaminants can enter water tanks through various sources such as rainwater, runoff, and improper maintenance. To identify and eliminate these health risks, regular water testing is essential. Testing can help determine the presence of contaminants and their levels, allowing for appropriate treatment measures to be implemented. Additionally, proper tank maintenance, such as regular cleaning and disinfection, can help prevent the buildup of contaminants and ensure the water remains safe for consumption.
Bacteria Contamination
Bacteria contamination in water tanks can lead to various health issues, including gastrointestinal illnesses. Common bacteria found in water tanks include E. coli, coliform bacteria, and Legionella. To prevent bacterial contamination, it is important to regularly clean and disinfect the water tank, ensure proper ventilation to prevent stagnation, and avoid cross-contamination from external sources. Installing a UV sterilizer or using chlorine tablets can also help eliminate bacteria in the water.
Heavy Metal Contamination
Heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and mercury can leach into water tanks from pipes, fittings, and other sources. Long-term exposure to heavy metals can lead to serious health problems, including neurological issues and organ damage. To reduce heavy metal contamination, it is important to use lead-free pipes and fittings, conduct regular water testing for heavy metals, and consider installing a water filtration system that can remove heavy metals from the water.
Chemical Contamination
Chemical contaminants in water tanks can come from pesticides, fertilizers, cleaning products, and other sources. These chemicals can have harmful effects on human health, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and even cancer. To reduce chemical contamination, it is important to store chemicals properly away from the water tank, use eco-friendly cleaning products, and consider installing a carbon filter or reverse osmosis system to remove chemicals from the water. Regular water testing can also help identify any chemical contaminants present in the water tank.
What are some common water tank contaminants that pose health risks?
Common water tank contaminants that pose health risks include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals. Bacteria such as E. coli and Legionella can cause gastrointestinal illnesses and respiratory infections, while viruses like norovirus and hepatitis A can lead to more serious health issues. Parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium can also cause gastrointestinal problems. Additionally, chemicals like lead, arsenic, and pesticides can contaminate water and have long-term health effects.
How can I identify if my water tank is contaminated?
There are several ways to identify if your water tank is contaminated. One common method is to look for signs of discoloration, odor, or taste in the water, which may indicate the presence of contaminants. You can also conduct water testing to determine the levels of bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals in your water. It is recommended to regularly test your water for contaminants, especially if you notice any changes in the water quality or if you live in an area with known water contamination issues.
What are the health risks associated with consuming contaminated water?
Consuming contaminated water can lead to a variety of health risks, depending on the type and level of contaminants present. Bacteria and viruses can cause gastrointestinal illnesses, respiratory infections, and other acute health issues. Parasites can also cause gastrointestinal problems and may be more difficult to treat. Chemical contaminants like lead, arsenic, and pesticides can have long-term health effects, including developmental delays, neurological disorders, and cancer. It is important to address water contamination promptly to prevent these health risks.
How can I eliminate contaminants from my water tank?
There are several methods to eliminate contaminants from your water tank. One common method is to use water filtration systems, such as activated carbon filters or reverse osmosis systems, to remove bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals from the water. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the water tank can also help prevent contamination. Additionally, treating the water with disinfectants like chlorine or UV light can kill bacteria and viruses. It is important to follow proper water treatment protocols to ensure the safety of your drinking water.
What are some preventive measures to reduce the risk of water tank contamination?
There are several preventive measures you can take to reduce the risk of water tank contamination. Regularly inspecting and maintaining your water tank can help prevent the buildup of contaminants. Keeping the tank covered and sealed properly can also prevent outside contaminants from entering the water. It is important to monitor the water quality and conduct regular testing to detect any contamination early. Educating yourself about common water tank contaminants and their health risks can also help you take proactive steps to protect your water supply.